Delving into the realm of health insurance premiums, this guide unveils the intricacies of comparing various plans to help you make informed decisions.
Exploring the nuances of premiums, types of plans, and key factors to consider, this discussion aims to empower you in navigating the complex world of health insurance.
Understanding Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are the amount of money that you pay to your insurance company in exchange for coverage of medical expenses. These premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on your policy.Factors that influence health insurance premiums:
Age and Gender
- Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums compared to older individuals.
- Women may have higher premiums due to maternity care costs.
Health History and Lifestyle
- Individuals with pre-existing conditions may have higher premiums.
- Smokers or individuals with unhealthy lifestyles may also face increased premiums.
Coverage and Deductibles
- Plans with more coverage and lower deductibles usually have higher premiums.
- High-deductible plans may have lower premiums but require higher out-of-pocket costs.
Location
- Healthcare costs can vary by region, impacting insurance premiums.
- Urban areas may have higher premiums compared to rural areas.
Employer-Sponsored vs. Individual Plans
- Employer-sponsored plans may offer lower premiums due to group rates.
- Individual plans may have higher premiums but offer more customization options.
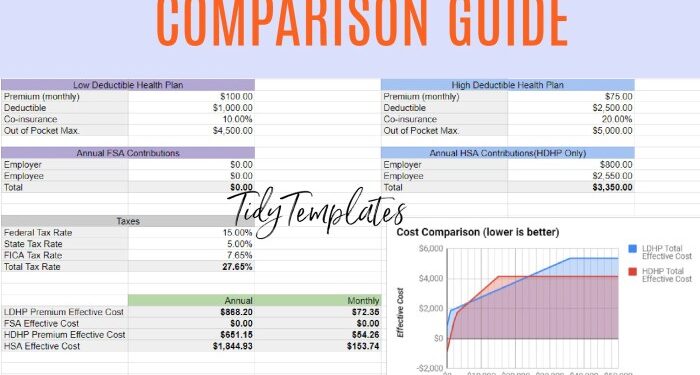
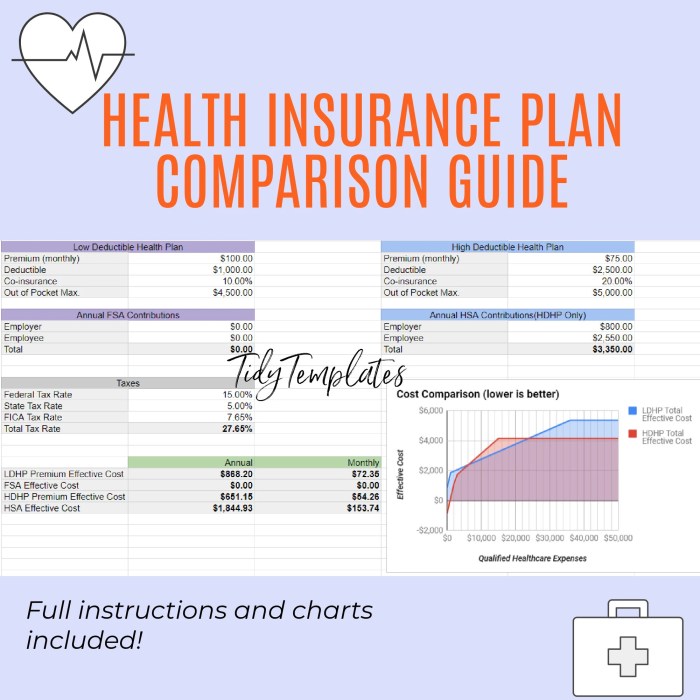
The importance of comparing health insurance premiums lies in finding the best value for your healthcare needs. By understanding the factors that influence premiums, you can make an informed decision when choosing a health insurance plan that suits your budget and coverage needs.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
When it comes to health insurance, there are several types of plans available. Each type offers different coverage options and comes with varying premium amounts based on the level of coverage provided.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
An HMO plan typically requires members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all of their healthcare needs. Referrals are usually needed to see specialists, and services outside the network may not be covered. HMO premiums are generally lower compared to other plans due to the restricted network and the need for referrals.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and do not require referrals to see specialists. Members can receive care from out-of-network providers, but at a higher cost. PPO premiums are typically higher than HMOs due to the increased flexibility and access to a broader network of providers.
High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)
HDHPs have higher deductibles and lower premiums compared to traditional plans. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) to help cover out-of-pocket costs. HDHP premiums are usually lower since the member is responsible for paying a higher deductible before insurance coverage kicks in.
Factors to Consider When Comparing Premiums
When comparing health insurance premiums, there are several key factors that individuals should take into consideration to ensure they are selecting the most suitable plan for their needs.
Coverage Limits
- Insurance premiums can vary based on the coverage limits provided by the plan. Plans with higher coverage limits typically have higher premiums as they offer more comprehensive coverage for medical expenses.
- Individuals should carefully assess their healthcare needs and choose a plan with coverage limits that align with their expected medical expenses.
Deductibles
- Deductibles are the amount of money individuals must pay out of pocket before their insurance coverage kicks in. Plans with lower deductibles usually have higher premiums, while plans with higher deductibles have lower premiums.
- It is important for individuals to consider their ability to cover the deductible amount when comparing premiums and selecting a plan.
Copayments
- Copayments are fixed amounts that individuals must pay for covered services after meeting their deductible. Plans with lower copayments often have higher premiums, while plans with higher copayments typically have lower premiums.
- Understanding the copayment structure of a plan is essential in determining the overall cost of healthcare services.
Age, Location, and Lifestyle Choices
- Age can significantly impact health insurance premiums, with older individuals generally paying higher premiums due to increased healthcare needs.
- Location also plays a role in premium costs, as healthcare costs can vary by region. Individuals living in areas with higher healthcare costs may face higher premiums.
- Lifestyle choices, such as smoking or engaging in high-risk activities, can also affect premium costs. Insurance companies may charge higher premiums to individuals with riskier lifestyles.
Tips for Comparing Health Insurance Premiums
When comparing health insurance premiums, it's important to consider various factors to ensure you find the best coverage at a reasonable cost. Here are some tips to help you navigate the process effectively.
1. Understand Your Needs
Before comparing premiums, assess your healthcare needs. Consider factors such as your medical history, any pre-existing conditions, and the frequency of doctor visits. This will help you determine the level of coverage you require.
2. Compare Coverage Options
When comparing premiums, don't just focus on the cost. Look at the coverage each plan offers, including services like hospital stays, prescription drugs, and preventive care. Make sure the plan aligns with your healthcare needs.
3. Utilize Online Tools
Take advantage of online resources to compare health insurance premiums. Use comparison websites or tools provided by insurance companies to get an overview of different plans available in your area. This can help you narrow down your options quickly.
4. Consider Cost-sharing Options
Look into cost-sharing options such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. While a plan with a lower premium may seem appealing, it could come with higher out-of-pocket costs. Find the right balance between premiums and potential expenses.
5. Evaluate Provider Networks
Check if your preferred healthcare providers are included in the plan's network. Choosing a plan with a broader network can give you more flexibility in selecting doctors and specialists. Ensure that the plan covers the healthcare facilities you trust.
6. Review Plan Benefits
Carefully review the benefits offered by each plan, including coverage for specific treatments, services, and medications. Look for any exclusions or limitations that may impact your healthcare needs. Choose a plan that provides comprehensive coverage.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of health insurance premiums is crucial for securing the right coverage at the best value. By following the tips and insights shared here, you are better equipped to make wise choices in safeguarding your health and finances.
Essential Questionnaire
What are health insurance premiums?
Health insurance premiums are the amount you pay to your insurance provider for coverage. They can vary based on the plan you choose and other factors.
How do different types of health insurance plans affect premiums?
The type of plan you choose can significantly impact your premium amount. Plans like HMOs, PPOs, and high-deductible health plans have varying premium costs.
What factors should individuals consider when comparing health insurance premiums?
When comparing premiums, consider factors like coverage limits, deductibles, copayments, as well as age, location, and lifestyle choices that can influence costs.
How can one effectively compare health insurance premiums?
By following a step-by-step guide, balancing coverage and cost considerations, and utilizing online tools, individuals can efficiently compare health insurance premiums to find the best option.